6 sampling methods|sampling techniques in statistics examples : consultant First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See more WEB6 de fev. de 2019 · Boomerang - Season 1 - TV Series | BET. A sequel to the 1992 movie, Boomerang takes a comedic look at the challenges of work-life balance in modern times. Watch Episodes. Episodes & Videos.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da The latest tweets from @FBITricolor
First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See more
Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that . See moreIn a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See moreIf you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. See more The best surveys keep target population at the core of their design. Learn about 6 effective sampling techniques that help you account for your population.
There are many different methods researchers can potentially use to obtain individuals to be in a sample. These are known as sampling methods. In this post we share the most commonly used sampling methods in .Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. Sampling methods. Sampling methods review. Samples and surveys.
types of sampling in biostatistics
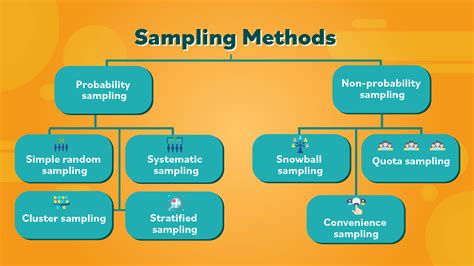
Sampling methods refer to the techniques used to select a subset of individuals or units from a larger population for the purpose of conducting statistical analysis or research. . Understand sampling methods in research, from simple random sampling to stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Learn how these sampling techniques boost data accuracy and representation, ensuring robust, .There are two major types of sampling methods: probability and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling, also known as random sampling, is a kind of sample selection where randomization is used instead of deliberate choice. .
This tutorial will introduce sampling methods and potential sampling errors to avoid when conducting medical research. Contents. Introduction to sampling methods; Examples of different sampling methods; . A sample is the subset of the population that you actually measure, test, or evaluate and base your results. Sampling methods are how you obtain your sample. Before beginning your study, carefully define the .Systematic sampling: The first person is selected randomly, and then a fixed interval is used to select additional individuals. For example, in a population of 1,000 people, the first selected individual is number 2 (shown in blue).; From .A visual representation of the sampling process. In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a statistical .
The sampling method is significant to strengthen the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the research results. One of the non-probability sampling techniques is .
Sampling Methods. The word population in statistics means the group of people we wish to study, as opposed to the population at large. When we use sampling to conduct a statistical study, first we need to decide how to choose the sample population. It is essential that the sample is a representative sample of the population we are studying. For example, if we .Simple random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting participants in a completely random fashion, where each participant has an equal chance of being selected.Basically, this sampling method is the equivalent of pulling names out of a hat, except that you can do it digitally.For example, if you had a list of 500 people, you could use a random .There are four types of probability sampling techniques: Simple random sampling: One of the best probability sampling techniques that helps in saving time and resources is the Simple Random Sampling method. It is a reliable method of obtaining information where every single member of a population is chosen randomly, merely by chance. Each . Stable Diffusionでは「Sampling method」によって狙った絵を出力できていないことは多く、この記事では画像生成時におけるSampling methodによる絵の変化と、おすすめのSampling methodについて紹介しています。
Read more: A Guide to Probability vs. Nonprobability Sampling Methods 5 types of probability sampling Here are the five types of probability sampling that researchers use: 1. Simple random sampling Simple random sampling, or SRS, occurs when each sample participant has the same probability of being chosen for the study. Consider a lottery method. A population is an entire group with specified characteristics. The target group/population is the desired population subgroup to be studied, and therefore want research findings to generalise to. A target group is usually too large to study in its entirety, so sampling methods are used to choose a representative sample from the target group.. A representative .
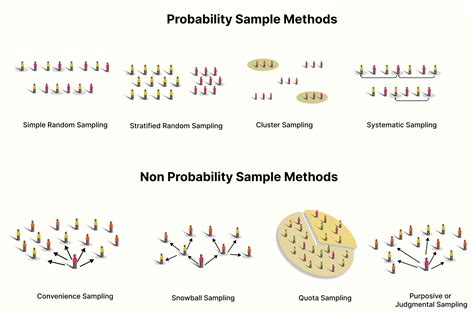
Probability sampling methods. Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice. There are four main types of .Choosing the right sampling method is a pivotal aspect of any research process, but it can be a stumbling block for many. Here’s a structured approach to guide your decision. 1) Define your research goals. If you aim to get a general sense of a larger group, simple random or stratified sampling could be your best bet. For focused insights or .Non-probability sampling methods. Non-probability sampling methods don’t offer the same bias-removal benefits as probability sampling, but there are times when these types of sampling are chosen for expediency or simplicity. Here are some forms of non-probability sampling and how they work. 1. Convenience sampling Sampling methods are the processes by which you draw a sample from a population. When performing research, you’re typically interested in the results for an entire population. Unfortunately, they are almost always too large to study fully. Consequently, researchers use samples to draw conclusions about a population—the process of making .
We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. Non-random sampling methods are liable to bias, and common examples include .
These techniques can be broadly categorised into two types: probability sampling techniques and non-probability sampling techniques. Probability sampling techniques include simple random sampling . Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration.
The National Field Manual for the Collection of Water-Quality Data (NFM) provides documented methods and protocols for USGS field personnel who collect water-quality data. The NFM provides detailed, comprehensive, and citable procedures for sampling water resources, processing samples for analysis of water quality, measuring field parameters, and specialized . 6.3 Sampling Types and Methods. There are two types of sampling, viz. probability sampling and non-probability sampling, and various subtypes are included in determining its sampling method as schematically represented in Fig. 6.1. We will try to learn its type and its method of application in detail with examples in various streams for allied .
As we delve into these categories, it’s essential to understand the nuances and applications of each method to ensure that the chosen sampling strategy aligns with the research goals. Probability sampling methods. There’s a wide range of probability sampling methods to explore and consider. Here are some of the best-known options. 1.
When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the .
As we delve into these categories, it’s essential to understand the nuances and applications of each method to ensure that the chosen sampling strategy aligns with the research goals. Probability sampling methods. There’s a wide range of probability sampling methods to explore and consider. Here are some of the best-known options. 1. Random Sampling is a method of probability sampling where a researcher randomly chooses a subset of individuals from a larger population.In this method, every individual has the same probability of being selected. The researcher aims to collect data from as large a portion as possible of this randomly chosen subset. Sampling methods are techniques used by researchers to select a smaller group of individuals or elements from a larger population. It’s like taking a small portion of something to represent the whole. Sampling methods help researchers . The selection of random type is done by probability random sampling while the non-selection type is by non-probability probability random sampling. This selection of techniques is talking about either without control (unrestricted) or with control (restricted) when individually the element of each sample is selected from a given totality, the .
Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for c . Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which researchers select members of the population at a regular interval (or k) determined in advance. If the population order is random or random-like (e.g., alphabetical), then this method will give you a representative sample that can be used to draw conclusions about your population of .Sampling is the statistical process of selecting a subset—called a ‘sample’—of a population of interest for the purpose of making observations and statistical inferences about that population. Social science research is generally about inferring patterns of behaviours within specific populations. We cannot study entire populations because of feasibility and cost constraints, .
type of sampling strategy
Categoria: Itens. Equipamento é um termo usado nesta wiki (.
6 sampling methods|sampling techniques in statistics examples